Direction of Dipole Rotation#
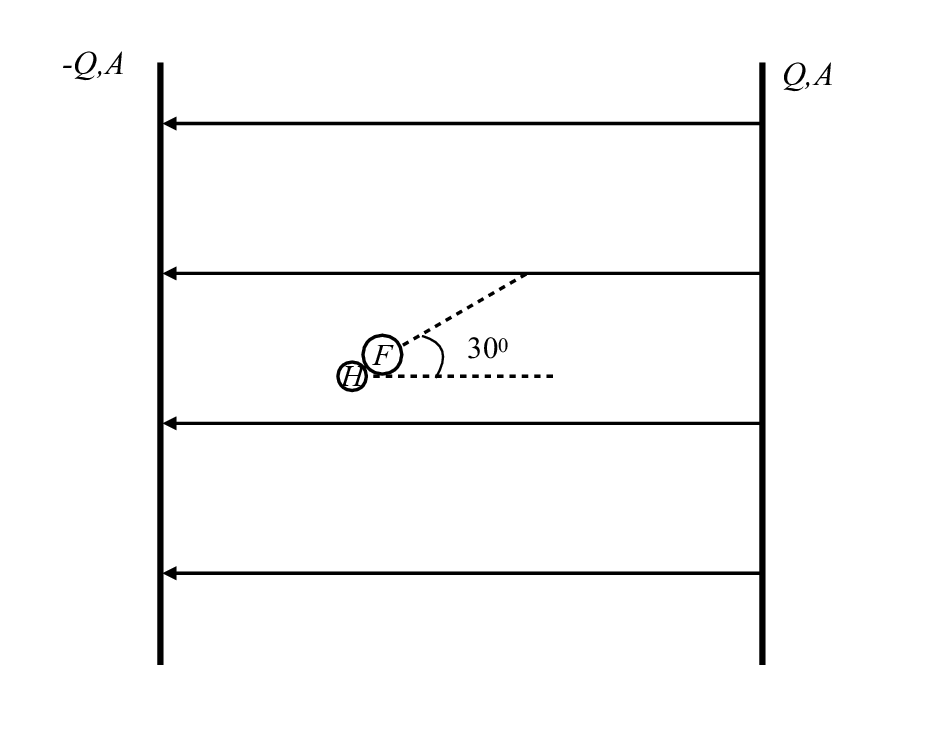
Hydrogen fluoride is a polar molecule with a bond length of about 0.92 x 10-10 m and can be roughly modeled as having a point charge of 6.6 x 10-20 C on the hydrogen atom and another of -6.6 x 10-20 C on the fluorine atom.
Part 1#
What will the HF molecule tend to do if placed in this geometry?
Answer Section#
Answer in 3-4 sentences, try and use full sentences.
Part 2#
A metal sphere is positively charged and has electric field lines as drawn.
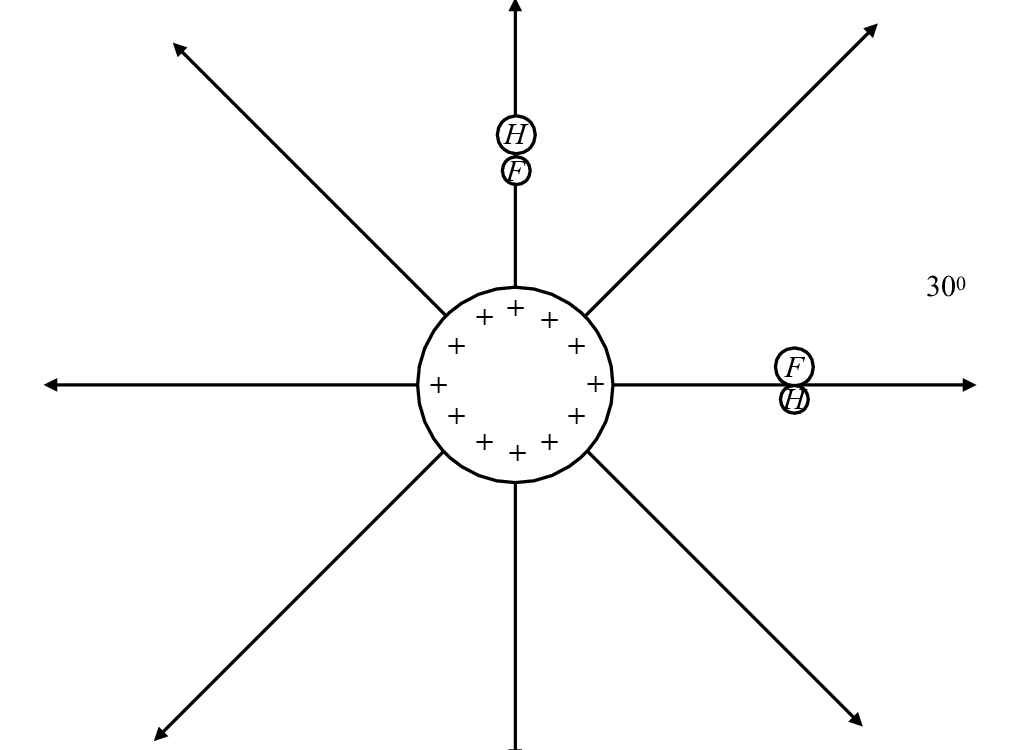
If the hydrogen fluoride molecule is placed with its axis along one of the field lines (above the sphere), which of the following statements are true?
Answer Section#
Note: You will be awarded full marks only if you select all the correct choices, and none of the incorrect choices. Choosing incorrect choices as well as not choosing correct choices will result in deductions.
The Hydrogen atom now experiences a weaker Electric Field
The Hydrogen atom now experiences a stronger Electric Field
The dipole experiences a net force towards the sphere
The dipole experiences a net force away from the sphere
The dipole will not experience a net torque as r and F are parallel
The dipole will experience a net torque as r and F are parallel
Part 3#
If the hydrogen fluoride molecule is placed with its axis perpendicular to the electric field lines, which of the following statements are correct?
Answer Section#
Note: You will be awarded full marks only if you select all the correct choices, and none of the incorrect choices. Choosing incorrect choices as well as not choosing correct choices will result in deductions.
There will be a small downward contribution to the net force
There will be a small upward contribution to the net force
The molecule experiences a net torque tending to rotate the dipole so that the F atom is closer to charged sphere
The molecule experiences a net torque tending to rotate the dipole so that the F atom is further away from charged sphere
Both forces have the same magnitude but not quite opposite directions
Both forces have the same magnitude and opposite directions
Attribution#
Problem is licensed under the CC-BY-NC-SA 4.0 license.